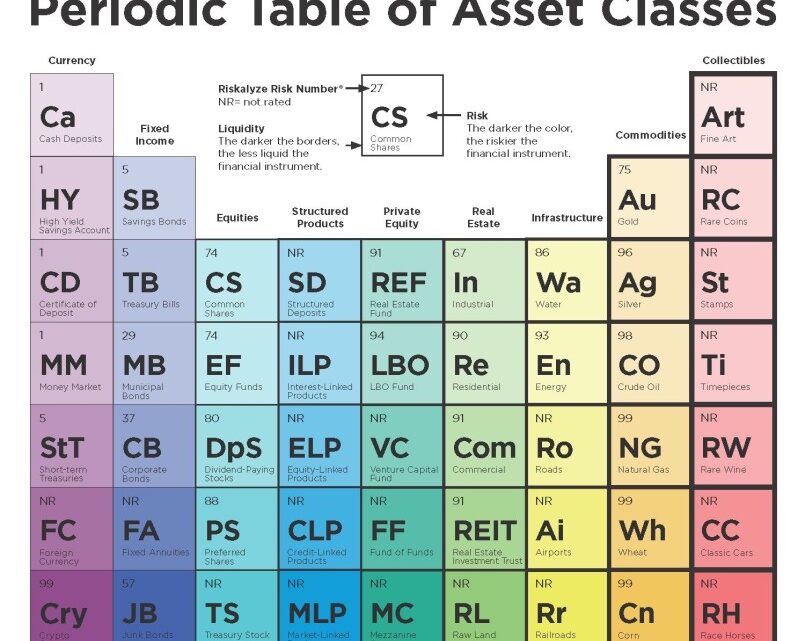
Investing can feel like navigating a maze, especially when you’re trying to balance returns and manage risk effectively. The secret to success lies in understanding the diverse range of asset classes available to you. Enter the “Periodic Table of Asset Classes,” a powerful visual guide that simplifies this complex landscape by categorizing assets based on risk, liquidity, and type.
Understanding Asset Classes
First things first—what exactly is an asset class? It’s a grouping of investments that behave similarly in the marketplace. These range from traditional categories like equities and bonds to alternative investments like real estate and commodities. Knowing the characteristics of each can significantly enhance your investment strategy.
The Visual Guide: Breaking Down the Periodic Table
The periodic table format offers a clear and comprehensive overview of various asset classes. Here’s a friendly breakdown to help you navigate:
1. Currency and Fixed Income:
– Ca (Cash Deposits): The safest asset class with high liquidity.
– HY (High Yield Savings Account) and CD (Certificate of Deposit): Slightly higher returns with minimal risk.
– SB (Savings Bonds) and TB (Treasury Bills): Government-backed, low-risk investments, ideal for conservative investors.
– MM (Money Market): Short-term, high-liquidity investments.
2. Bonds:
– MB (Municipal Bonds) and CB (Corporate Bonds): Offer tax benefits and higher yields with varying degrees of risk.
– JB (Junk Bonds): High-risk, high-yield options for the daring investor.
3. Equities:
– CS (Common Shares) and EF (Equity Funds): Ownership in companies with higher risk and potential returns.
– DPS (Dividend-Paying Stocks): Provide regular income with a touch of stability.
4. Structured Products and Private Equity:
– SD (Structured Products) and ILP (Interest-Linked Products): Customized investments tailored to specific risk-return profiles.
– REF (Real Estate Fund) and LBO (Leveraged Buyout Fund): Exposure to private companies and real estate.
5. Real Estate and Infrastructure:
– Re (Residential) and Com (Commercial): Physical properties offering income and potential appreciation.
– En (Energy), Wa (Water), and Ai (Airports): Critical infrastructure investments with varying stability and returns.
6. Commodities and Collectibles:
– Au (Gold), Ag (Silver), and CO (Crude Oil): Tangible assets that hedge against inflation.
– Art, RC (Rare Coins), and St (Stamps): Unique investments driven by rarity and demand.
Navigating Risk and Liquidity
The Riskalyze Risk Number® is your friend here, indicating the risk level with higher numbers signifying greater risk. Liquidity is shown by the darkness of the borders: the darker the border, the less liquid the asset.
– Low-Risk, High-Liquidity: Cash deposits (Ca) and Treasury bills (TB) are perfect for risk-averse investors.
– High-Risk, Low-Liquidity: Cryptocurrencies (Cry) and collectibles like art (Art) promise high returns but come with significant risk and liquidity challenges.
Building a Balanced Portfolio
Creating a well-balanced portfolio means spreading your investments across various asset classes. Conservative investors might favor bonds and cash equivalents, while aggressive investors might lean towards equities and alternative assets. The key is diversification, which helps manage risk and enhance returns.
Conclusion
The Periodic Table of Asset Classes is a treasure trove for both novice and seasoned investors. It offers a clear snapshot of the investment universe, aiding in making informed decisions based on your risk tolerance and financial goals. By diversifying across various asset classes, you can better navigate the financial markets and work towards achieving your long-term objectives.
Stay connected with me for more insights, tips, and comprehensive guides on navigating the financial world. Join our community of savvy investors and boost your financial literacy with engaging and informative content. Let’s embark on this journey to financial success together!